Linux内核源码阅读

内核源码阅读
- 源码版本: Linux 4.0.0
- 参考书籍:
- « 奔跑吧Linux内核 »
- « 深度探索linux系统虚拟化:原理与实现 »
1 建立环境
1.1 崩溃内核
1.1.1 安装拯救内核
下载内核稳定版,修改构建脚本为了和主线内核区分即可
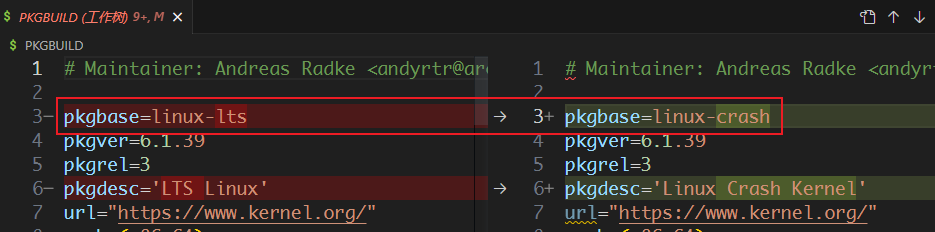
修改配置脚本config
CONFIG_DEBUG_INFO=y
CONFIG_CRASH_DUMP=y
CONFIG_PROC_VMCORE=y构建此内核
# 更新校验值
updpkgsums
# 构建内核
makepkg -s --skippgpcheck
# 安装程序修改/etc/default/grub,为crash kernel配置空间
- GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="loglevel=7"
+ GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="loglevel=7 crashkernel=256M@16M"
更新grub配置grub-mkconfig
1.1.2 启动kdump服务
/etc/systemd/system/kdump.service
[Unit]
Description=Load dump capture kernel
After=local-fs.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/kexec -p [/boot/vmlinuz-linux-kdump] --initrd=[/boot/initramfs-linux-kdump.img] --append="root=[root-device] single irqpoll maxcpus=1 reset_devices"
Type=oneshot
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target1.2 基础环境
- 安装软件
$ sudo apt install qemu
$ sudo apt install gcc-arm-none-eabi- 下载源码
$ git clone https://github.com/figozhang/runninglinuxkernel_4.0.git- 构建运行
- 编译32位arm
qemu-system-arm -m 1024 -M virt\
-nographic -smp 4 -kernel arch/arm/boot/zImage \
-append "crashkernel=128M root=/dev/vda rootfstype=ext4 rw"\
-drive if=none,file=rootfs_debian_arm32.ext4,id=hd0 \
-device virtio-blk-device,drive=hd0 \
-netdev user,id=mynet\
-device virtio-net-device,netdev=mynet\
--fsdev local,id=kmod_dev,path=./kmodules,security_model=none\
-device virtio-9p-device,fsdev=kmod_dev,mount_tag=kmod_mount\
-S -s- 编译64位arm
qemu-system-aarch64 -m 1024 -cpu cortex-a57 -M virt\
-nographic -smp 4 -kernel arch/arm64/boot/Image \
-append "noinintrd root=/dev/vda rootfstype=ext4 rw loglevel=8" \
-drive if=none,file=rootfs_debian_arm64.ext4,id=hd0 \
-device virtio-blk-device,drive=hd0 \
--fsdev local,id=kmod_dev,path=./kmodules,security_model=none \
-device virtio-9p-device,fsdev=kmod_dev,mount_tag=kmod_mount\
-netdev user,id=mynet\
-device virtio-net-device,netdev=mynet\
-S -s- 安装gdb-multiarch
# 下载代码
git clone --branch gdb-13-branch https://sourceware.org/git/binutils-gdb.git
# 执行构建
mkdir build && cd build
../configure \
--enable-targets=all \
--prefix=/build \
--enable-languages=all \
--enable-multilib \
--enable-interwork \
--with-system-readline \
--disable-nls \
--with-python=/usr/bin/python \
--with-system-gdbinit=/etc/gdb/gdbinit
make -j`nproc`
make install
# 修改文件名
mv /usr/bin/gdb /usr/bin/gdb-multiarch- 运行gdb-multiarch
# 加载执行文件
$ file vmlinux
# 设置架构
$ set architecture arm
# 远程连接
$ target remote localhost:12341.3 调试环境(eclipse)
- 安装eclipse
- 安装jdk
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install default-jre- 下载eclipse C/C++
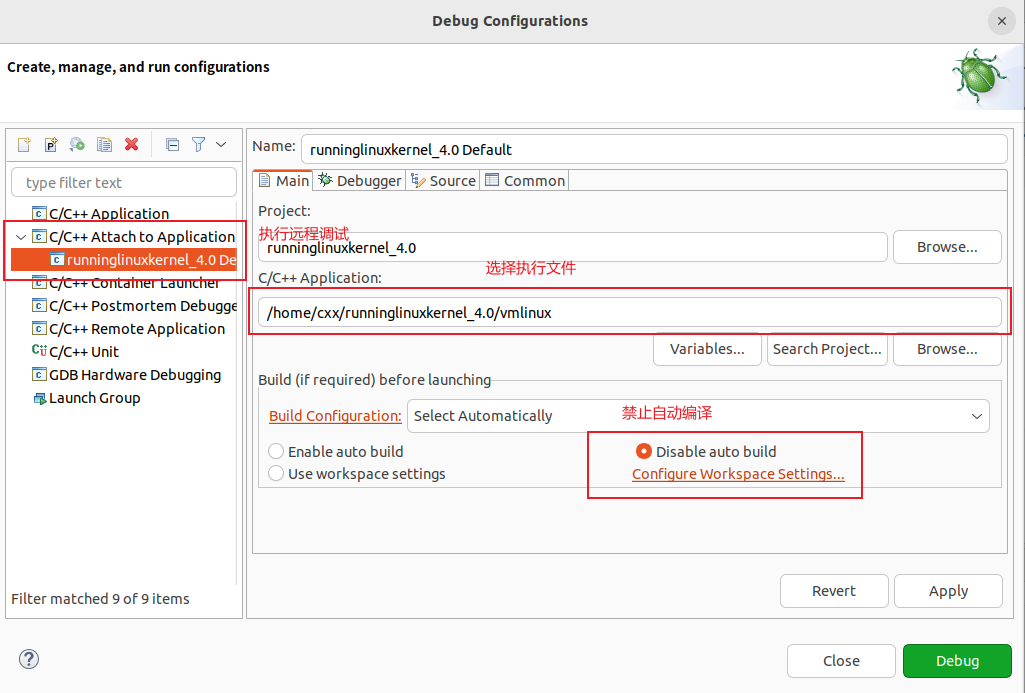
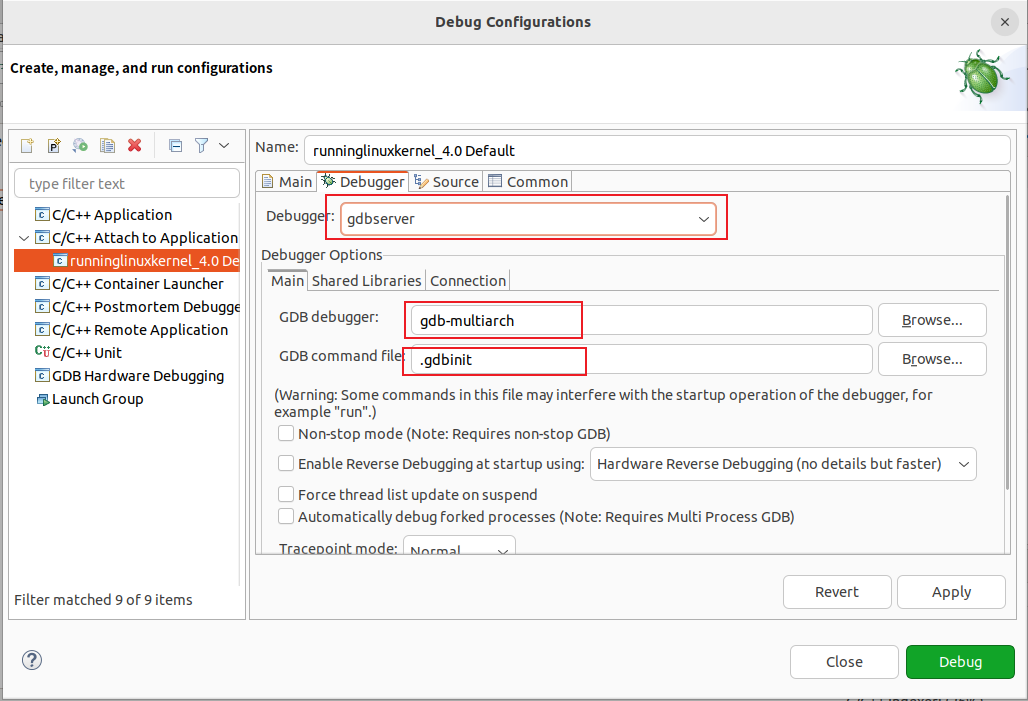
- 配置调试
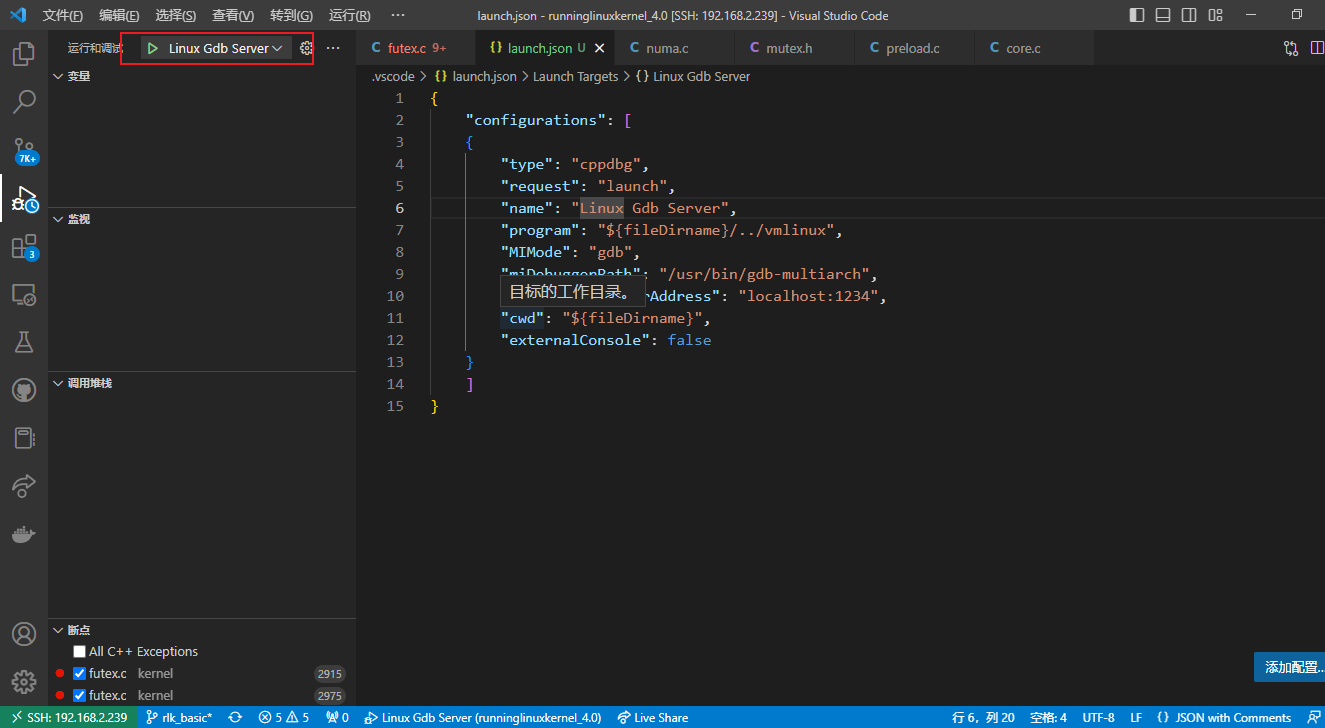
1.4 调试环境(vscode)
当然vscode也是相当好用的,作为调试程序
- 在当前工程中添加配置文件launch.json
{
"configurations": [
{
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"name": "Linux Gdb Server",
"program": "${workspaceRoot}/vmlinux",
"MIMode": "gdb",
"miDebuggerPath": "/usr/bin/gdb-multiarch",
"miDebuggerServerAddress": "localhost:1234",
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}",
"externalConsole": false
}
]
}- 安装调试器
yay -S gdb-multiarch- 启动调试器
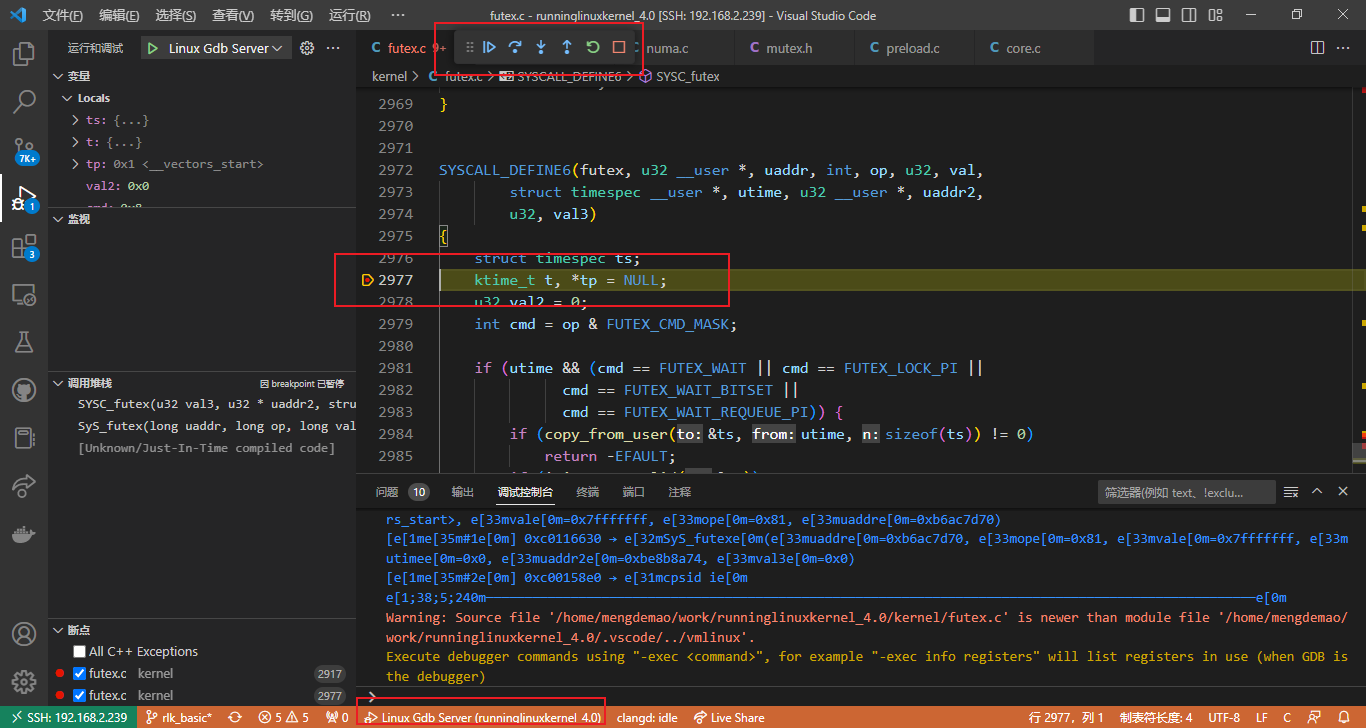
1.5 调试环境(原始gdb)
- 安装gdbgui
# 安装
pip install gdbgui
# 设计
pip install --upgrade gdbgui
# 卸载
$ pip uninstall gdbgui- 运行gdbgui
gdbgui -g arm-multiarch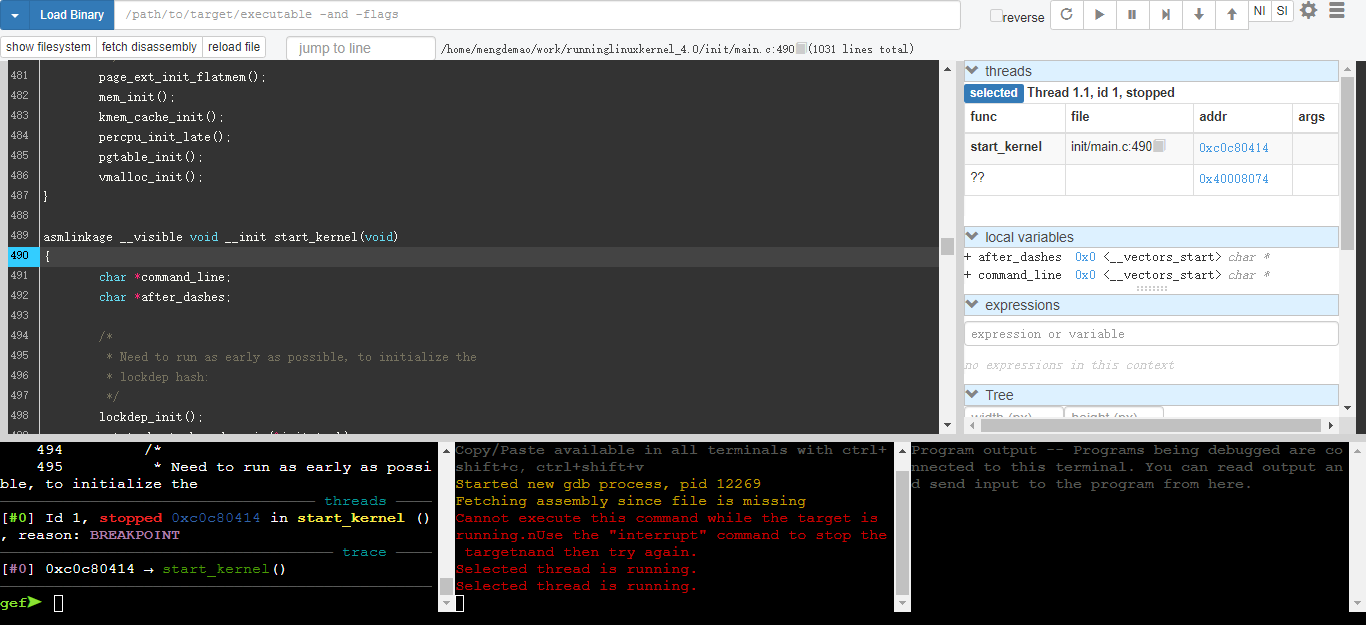
2 系统构建
镜像文件的整体过程
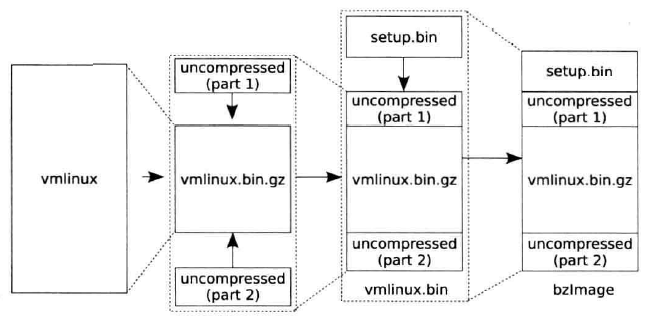
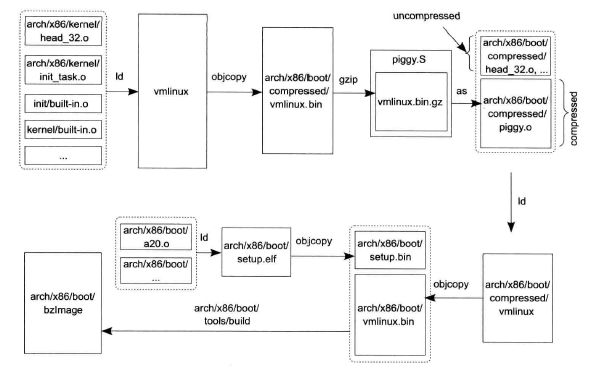
- 构建vmlinux,objcopy生成vmlinux.bin,然后将其压缩为vmlinux.bin.gz
- 添加操作,生成vmlinux.bin
- 构造setup.bin
- 将setup.bin与vmlinux.bin进行合成,生成bzImage
2.1 vmlinux生成过程
# x86_64架构链接过程
ld -m elf_x86_64 --no-ld-generated-unwind-info -pie --no-dynamic-linker --orphan-handling=error -z noexecstack --no-warn-rwx-segments
-T arch/x86/boot/compressed/vmlinux.lds
arch/x86/boot/compressed/kernel_info.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/head_64.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/misc.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/string.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/cmdline.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/error.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/piggy.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/cpuflags.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/early_serial_console.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/kaslr.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/ident_map_64.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/idt_64.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/idt_handlers_64.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/pgtable_64.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/acpi.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/efi.o arch/x86/boot/compressed/efi_mixed.o drivers/firmware/efi/libstub/lib.a
-o arch/x86/boot/compressed/vmlinux
# arm32链接过程2.2 vmlinux.bin生成过程
objcopy -O binary -R .note -R .comment -S arch/x86/boot/compressed/vmlinux arch/x86/boot/vmlinux.bin2.3 header.o
gcc -Wp,-MMD,arch/x86/boot/.header.o.d -nostdinc -I./arch/x86/include -I./arch/x86/include/generated -I./include -I./arch/x86/include/uapi -I./arch/x86/include/generated/uapi -I./include/uapi -I./include/generated/uapi -include ./include/linux/compiler-version.h -include ./include/linux/kconfig.h -D__KERNEL__ -Werror -fmacro-prefix-map=./= -m16 -g -Os -DDISABLE_BRANCH_PROFILING -D__DISABLE_EXPORTS -Wall -Wstrict-prototypes -march=i386 -mregparm=3 -fno-strict-aliasing -fomit-frame-pointer -fno-pic -mno-mmx -mno-sse -fcf-protection=none -ffreestanding -fno-stack-protector -Wno-address-of-packed-member -mpreferred-stack-boundary=2 -D_SETUP -D__ASSEMBLY__ -DSVGA_MODE=NORMAL_VGA -I./arch/x86/boot -c -o arch/x86/boot/header.o arch/x86/boot/header.S2.4 setup.bin生成过程
ld -m elf_x86_64 -z noexecstack --no-warn-rwx-segments -m elf_i386 -z noexecstack -T arch/x86/boot/setup.ld arch/x86/boot/a20.o arch/x86/boot/bioscall.o arch/x86/boot/cmdline.o arch/x86/boot/copy.o arch/x86/boot/cpu.o arch/x86/boot/cpuflags.o arch/x86/boot/cpucheck.o arch/x86/boot/early_serial_console.o arch/x86/boot/edd.o arch/x86/boot/header.o arch/x86/boot/main.o arch/x86/boot/memory.o arch/x86/boot/pm.o arch/x86/boot/pmjump.o arch/x86/boot/printf.o arch/x86/boot/regs.o arch/x86/boot/string.o arch/x86/boot/tty.o arch/x86/boot/video.o arch/x86/boot/video-mode.o arch/x86/boot/version.o arch/x86/boot/video-vga.o arch/x86/boot/video-vesa.o arch/x86/boot/video-bios.o -o arch/x86/boot/setup.elf
objcopy -O binary arch/x86/boot/setup.elf arch/x86/boot/setup.bin2.5 最后生成
arch/x86/boot/tools/build arch/x86/boot/setup.bin arch/x86/boot/vmlinux.bin arch/x86/boot/zoffset.h arch/x86/boot/bzImag3 根文件系统
linux系统在启动之后需要加载根文件系统
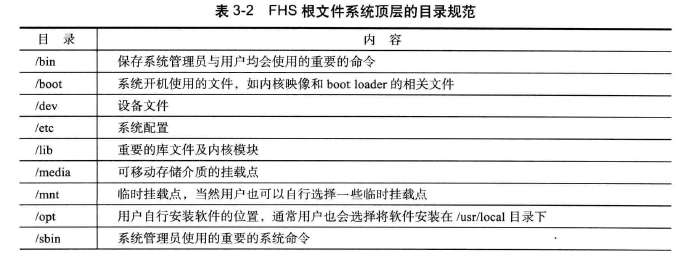
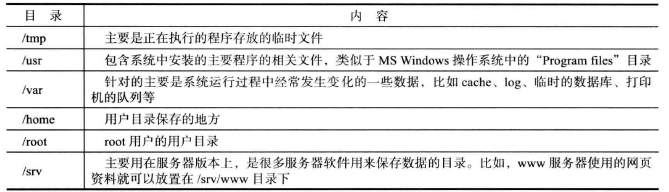
3.1 编译busybox
3.2 安装C库
从交叉编译器中拷贝即可
4 initramfs
4.1 Hello initramfs
#include <stdio.h>
void main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
printf("Hello initramfs\n");
fflush(stdout);
while(1);
}执行构建
gcc -static -o init init.c
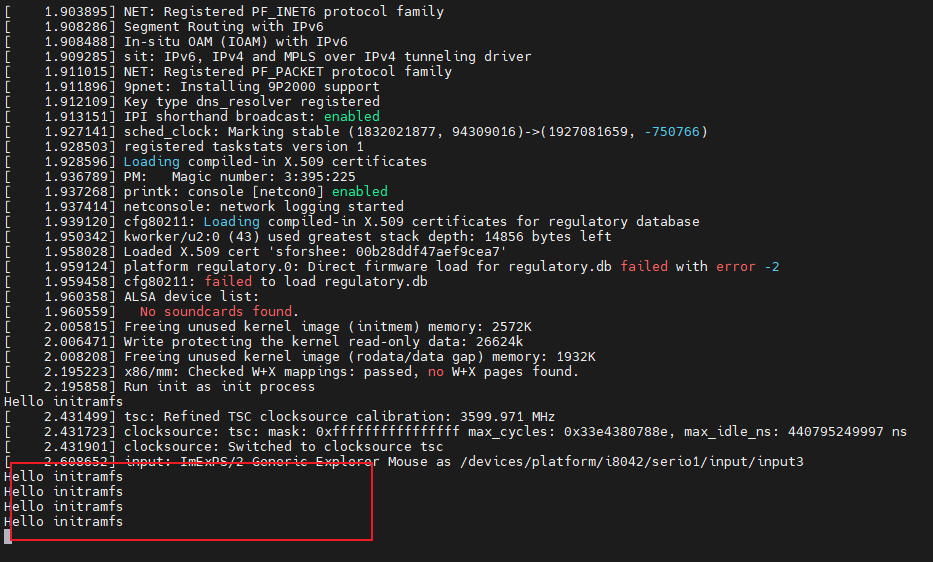
echo init | cpio -o --format=newc > initramfs启动测试
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel linux/arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage -initrd initramfs -append "console=ttyS0 rdinit=init" -nographic然后就可以发现打印的数据
5 启动分析
一般情况下,我们都会讲断点打在start_kernel上,但是在进入C语言之前会存在一段汇编代码;
入口地址,我们可以通过链接脚本分析得到
链接头文件,那么真正的链接文件在**[arch/arm/kernel/vmlinux.lds]**,但是这个文件是生成的;
这个链接脚本用来描述vmlinux的生成
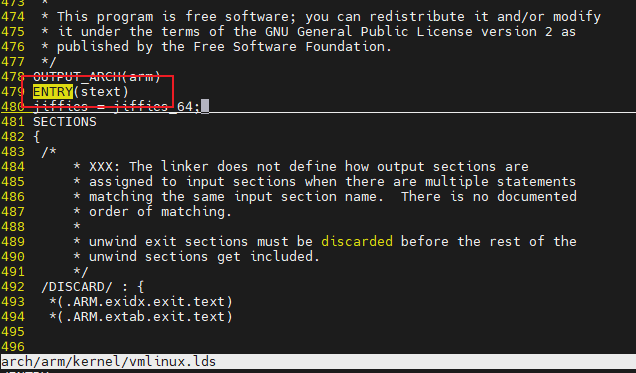
但是aarch64入口地址就是
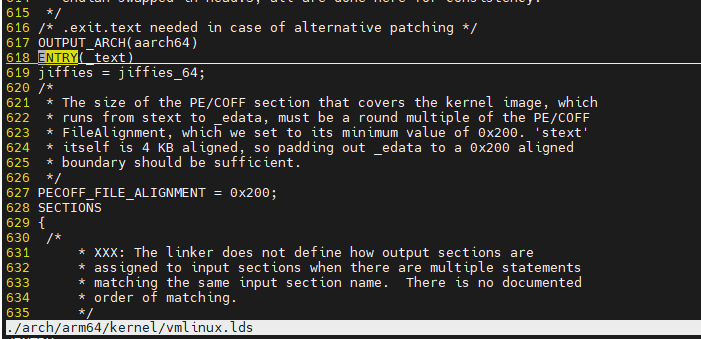
graph LR stext --> __mmap_switched __mmap_switched --> start_kernel
5.1 启动前夕
启动前夕(ARM32)
__mmap_switched:
adr r3, __mmap_switched_data
ldmia r3!, {r4, r5, r6, r7}
cmp r4, r5 @ Copy data segment if needed
1: cmpne r5, r6
ldrne fp, [r4], #4
strne fp, [r5], #4
bne 1b
mov fp, #0 @ Clear BSS (and zero fp)
1: cmp r6, r7
strcc fp, [r6],#4
bcc 1b
ARM( ldmia r3, {r4, r5, r6, r7, sp})
THUMB( ldmia r3, {r4, r5, r6, r7} )
THUMB( ldr sp, [r3, #16] )
str r9, [r4] @ Save processor ID
str r1, [r5] @ Save machine type
str r2, [r6] @ Save atags pointer
cmp r7, #0
strne r0, [r7] @ Save control register values
b start_kernel
ENDPROC(__mmap_switched)启动前夕(ARM64)
__mmap_switched:
adr x3, __switch_data + 8
ldp x6, x7, [x3], #16
1: cmp x6, x7
b.hs 2f
str xzr, [x6], #8 // Clear BSS
b 1b
2:
ldp x4, x5, [x3], #16
ldr x6, [x3], #8
ldr x16, [x3]
mov sp, x16
str x22, [x4] // Save processor ID
str x21, [x5] // Save FDT pointer
str x24, [x6] // Save PHYS_OFFSET
mov x29, #0
b start_kernel
ENDPROC(__mmap_switched)
.align 3
.type __switch_data, %object
__switch_data:
.quad __mmap_switched
.quad __bss_start // x6
.quad __bss_stop // x7
.quad processor_id // x4
.quad __fdt_pointer // x5
.quad memstart_addr // x6
.quad init_thread_union + THREAD_START_SP // sp
ENTRY(stext)
mov x21, x0 // x21=FDT
bl el2_setup // Drop to EL1, w20=cpu_boot_mode
bl __calc_phys_offset // x24=PHYS_OFFSET, x28=PHYS_OFFSET-PAGE_OFFSET
bl set_cpu_boot_mode_flag
mrs x22, midr_el1 // x22=cpuid
mov x0, x22
bl lookup_processor_type
mov x23, x0 // x23=current cpu_table
/*
* __error_p may end up out of range for cbz if text areas are
* aligned up to section sizes.
*/
cbnz x23, 1f // invalid processor (x23=0)?
b __error_p
1:
bl __vet_fdt
bl __create_page_tables // x25=TTBR0, x26=TTBR1
/*
* The following calls CPU specific code in a position independent
* manner. See arch/arm64/mm/proc.S for details. x23 = base of
* cpu_info structure selected by lookup_processor_type above.
* On return, the CPU will be ready for the MMU to be turned on and
* the TCR will have been set.
*/
ldr x27, __switch_data // address to jump to after
// MMU has been enabled
adrp lr, __enable_mmu // return (PIC) address
add lr, lr, #:lo12:__enable_mmu
ldr x12, [x23, #CPU_INFO_SETUP]
add x12, x12, x28 // __virt_to_phys
br x12 // initialise processor
ENDPROC(stext)上面的汇编函数都是由head.s跳入继续向下分析,谁开启了汇编,如何执行到这个函数vmlinux.lds决定,分析实现;
需要分析bootloader的实现;
下面我们开始分析
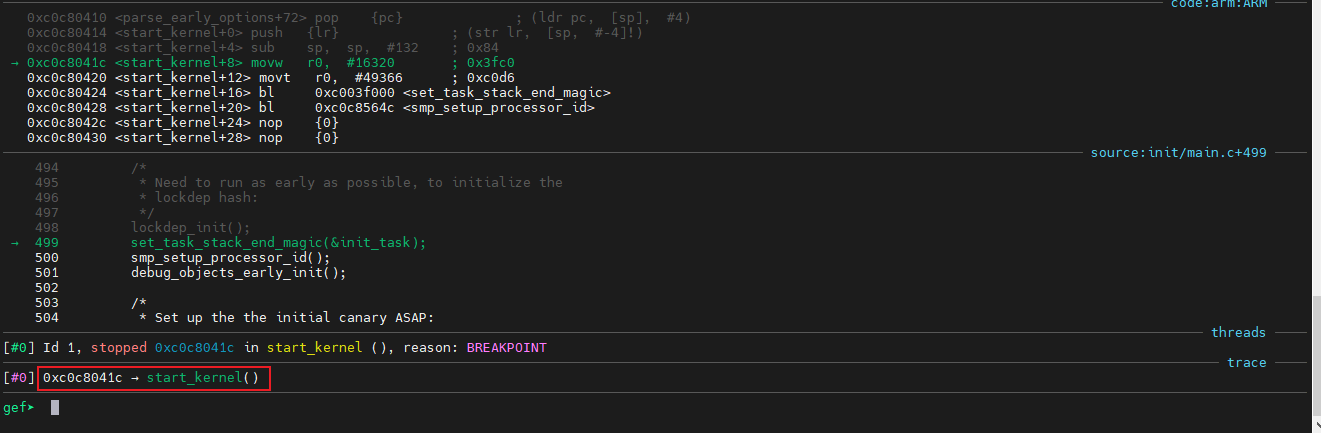
5.2 start_kernel
进入内核中第一个C语言启动函数;源码位置
asmlinkage __visible void __init start_kernel(void)
{
char *command_line;
char *after_dashes;
// 死锁检测
lockdep_init();
// 设置启动任务的结束磨数
set_task_stack_end_magic(&init_task);
// 设置smp id
smp_setup_processor_id();
// debug
debug_objects_early_init();
// 堆栈保护机制
boot_init_stack_canary();
// cgroup初始化
cgroup_init_early();
// irq中断停止,设置标志位
local_irq_disable();
early_boot_irqs_disabled = true;
// 激活启动CPU
boot_cpu_init();
// 单独章节分析
page_address_init();
pr_notice("%s", linux_banner);
// 设置架构
setup_arch(&command_line);
mm_init_cpumask(&init_mm);
setup_command_line(command_line);
setup_nr_cpu_ids();
setup_per_cpu_areas();
smp_prepare_boot_cpu(); /* arch-specific boot-cpu hooks */
build_all_zonelists(NULL, NULL);
page_alloc_init();
pr_notice("Kernel command line: %s\n", boot_command_line);
parse_early_param();
after_dashes = parse_args("Booting kernel",
static_command_line, __start___param,
__stop___param - __start___param,
-1, -1, &unknown_bootoption);
if (!IS_ERR_OR_NULL(after_dashes))
parse_args("Setting init args", after_dashes, NULL, 0, -1, -1,
set_init_arg);
jump_label_init();
/*
* These use large bootmem allocations and must precede
* kmem_cache_init()
*/
setup_log_buf(0);
pidhash_init();
vfs_caches_init_early();
sort_main_extable();
trap_init();
mm_init();
/*
* Set up the scheduler prior starting any interrupts (such as the
* timer interrupt). Full topology setup happens at smp_init()
* time - but meanwhile we still have a functioning scheduler.
*/
sched_init();
/*
* Disable preemption - early bootup scheduling is extremely
* fragile until we cpu_idle() for the first time.
*/
preempt_disable();
if (WARN(!irqs_disabled(),
"Interrupts were enabled *very* early, fixing it\n"))
local_irq_disable();
idr_init_cache();
rcu_init();
/* trace_printk() and trace points may be used after this */
trace_init();
context_tracking_init();
radix_tree_init();
/* init some links before init_ISA_irqs() */
early_irq_init();
init_IRQ();
tick_init();
rcu_init_nohz();
init_timers();
hrtimers_init();
softirq_init();
timekeeping_init();
time_init();
sched_clock_postinit();
perf_event_init();
profile_init();
call_function_init();
WARN(!irqs_disabled(), "Interrupts were enabled early\n");
early_boot_irqs_disabled = false;
local_irq_enable();
kmem_cache_init_late();
/*
* HACK ALERT! This is early. We're enabling the console before
* we've done PCI setups etc, and console_init() must be aware of
* this. But we do want output early, in case something goes wrong.
*/
console_init();
if (panic_later)
panic("Too many boot %s vars at `%s'", panic_later,
panic_param);
lockdep_info();
/*
* Need to run this when irqs are enabled, because it wants
* to self-test [hard/soft]-irqs on/off lock inversion bugs
* too:
*/
locking_selftest();
#ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_INITRD
if (initrd_start && !initrd_below_start_ok &&
page_to_pfn(virt_to_page((void *)initrd_start)) < min_low_pfn) {
pr_crit("initrd overwritten (0x%08lx < 0x%08lx) - disabling it.\n",
page_to_pfn(virt_to_page((void *)initrd_start)),
min_low_pfn);
initrd_start = 0;
}
#endif
page_ext_init();
debug_objects_mem_init();
kmemleak_init();
setup_per_cpu_pageset();
numa_policy_init();
if (late_time_init)
late_time_init();
sched_clock_init();
calibrate_delay();
pidmap_init();
anon_vma_init();
acpi_early_init();
#ifdef CONFIG_X86
if (efi_enabled(EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES))
efi_enter_virtual_mode();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_X86_ESPFIX64
/* Should be run before the first non-init thread is created */
init_espfix_bsp();
#endif
thread_info_cache_init();
cred_init();
fork_init(totalram_pages);
proc_caches_init();
buffer_init();
key_init();
security_init();
dbg_late_init();
vfs_caches_init(totalram_pages);
signals_init();
/* rootfs populating might need page-writeback */
page_writeback_init();
proc_root_init();
nsfs_init();
cgroup_init();
cpuset_init();
taskstats_init_early();
delayacct_init();
check_bugs();
sfi_init_late();
if (efi_enabled(EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES)) {
efi_late_init();
efi_free_boot_services();
}
ftrace_init();
/* Do the rest non-__init'ed, we're now alive */
rest_init();
}但是谁调用了此函数呢?
5.3 reset_init
这个是系统调用的最后一个函数,调用结束后不会返回
static noinline void __init_refok rest_init(void)
{
int pid;
rcu_scheduler_starting();
/*
* We need to spawn init first so that it obtains pid 1, however
* the init task will end up wanting to create kthreads, which, if
* we schedule it before we create kthreadd, will OOPS.
*/
kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS);
numa_default_policy();
pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);
rcu_read_lock();
kthreadd_task = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns);
rcu_read_unlock();
complete(&kthreadd_done);
/*
* The boot idle thread must execute schedule()
* at least once to get things moving:
*/
init_idle_bootup_task(current);
schedule_preempt_disabled();
/* Call into cpu_idle with preempt disabled */
cpu_startup_entry(CPUHP_ONLINE);
}5.4 设置init任务堆栈
set_task_stack_end_magic(&init_task);
void set_task_stack_end_magic(struct task_struct *tsk)
{
unsigned long *stackend;
stackend = end_of_stack(tsk);
*stackend = STACK_END_MAGIC; /* for overflow detection */
}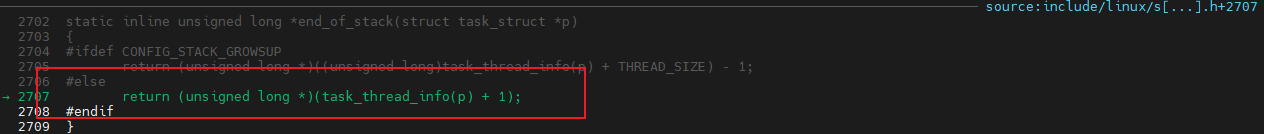
此处可以得知:
static inline unsigned long *end_of_stack(struct task_struct *p)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_STACK_GROWSUP
return (unsigned long *)((unsigned long)task_thread_info(p) + THREAD_SIZE) - 1;
#else
return (unsigned long *)(task_thread_info(p) + 1);
#endif
}5.5 设置smp的CPU ID
int nr_cpu_ids __read_mostly = NR_CPUS; // 此参数通过配置文件得到
EXPORT_SYMBOL(nr_cpu_ids);
u32 __cpu_logical_map[NR_CPUS] = { [0 ... NR_CPUS-1] = MPIDR_INVALID };
#define cpu_logical_map(cpu) __cpu_logical_map[cpu]
// 1. 设置cpu_logical_map
// 2. 设置线程ID
// 3. 打印日志
void __init smp_setup_processor_id(void)
{
int i;
u32 mpidr = is_smp() ? read_cpuid_mpidr() & MPIDR_HWID_BITMASK : 0;
u32 cpu = MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 0);
cpu_logical_map(0) = cpu;
for (i = 1; i < nr_cpu_ids; ++i)
cpu_logical_map(i) = i == cpu ? 0 : i;
/*
* clear __my_cpu_offset on boot CPU to avoid hang caused by
* using percpu variable early, for example, lockdep will
* access percpu variable inside lock_release
*/
set_my_cpu_offset(0);
pr_info("Booting Linux on physical CPU 0x%x\n", mpidr);
}
// 设置线程ID
static inline void set_my_cpu_offset(unsigned long off)
{
/* Set TPIDRPRW */
// off=0x0
asm volatile("mcr p15, 0, %0, c13, c0, 4" : : "r" (off) : "memory");
}5.6 激活启动CPU
static void __init boot_cpu_init(void)
{
int cpu = smp_processor_id();
/* Mark the boot cpu "present", "online" etc for SMP and UP case */
set_cpu_online(cpu, true);
set_cpu_active(cpu, true);
set_cpu_present(cpu, true);
set_cpu_possible(cpu, true);
}5.7 设置架构
读取配置文件(设置树),设置内存信息
在设备树一章节中会详细分析
void __init setup_arch(char **cmdline_p)
{
// 机器描述符
const struct machine_desc *mdesc;
// 设置处理器相关信息
setup_processor();
// 读取设备树信息
mdesc = setup_machine_fdt(__atags_pointer);
if (!mdesc)
mdesc = setup_machine_tags(__atags_pointer, __machine_arch_type);
// 设置到全局变量
machine_desc = mdesc;
machine_name = mdesc->name;
dump_stack_set_arch_desc("%s", mdesc->name);
if (mdesc->reboot_mode != REBOOT_HARD)
reboot_mode = mdesc->reboot_mode;
// 设置init任务
init_mm.start_code = (unsigned long) _text;
init_mm.end_code = (unsigned long) _etext;
init_mm.end_data = (unsigned long) _edata;
init_mm.brk = (unsigned long) _end;
/* populate cmd_line too for later use, preserving boot_command_line */
strlcpy(cmd_line, boot_command_line, COMMAND_LINE_SIZE);
*cmdline_p = cmd_line;
parse_early_param();
// 读取设备树
early_paging_init(mdesc, lookup_processor_type(read_cpuid_id()));
setup_dma_zone(mdesc);
sanity_check_meminfo();
arm_memblock_init(mdesc);
paging_init(mdesc);
request_standard_resources(mdesc);
if (mdesc->restart)
arm_pm_restart = mdesc->restart;
unflatten_device_tree();
arm_dt_init_cpu_maps();
psci_init();
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
if (is_smp()) {
if (!mdesc->smp_init || !mdesc->smp_init()) {
if (psci_smp_available())
smp_set_ops(&psci_smp_ops);
else if (mdesc->smp)
smp_set_ops(mdesc->smp);
}
smp_init_cpus();
smp_build_mpidr_hash();
}
#endif
if (!is_smp())
hyp_mode_check();
reserve_crashkernel();
#ifdef CONFIG_MULTI_IRQ_HANDLER
handle_arch_irq = mdesc->handle_irq;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_VT
#if defined(CONFIG_VGA_CONSOLE)
conswitchp = &vga_con;
#elif defined(CONFIG_DUMMY_CONSOLE)
conswitchp = &dummy_con;
#endif
#endif
if (mdesc->init_early)
mdesc->init_early();
}5.8 mm_init_cpumask
清理内存管理系统的init_mm->cpu_vm_mask_var
static inline void mm_init_cpumask(struct mm_struct *mm)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_CPUMASK_OFFSTACK
mm->cpu_vm_mask_var = &mm->cpumask_allocation;
#endif
cpumask_clear(mm->cpu_vm_mask_var);
}5.9 设置命令行command_line
申请内存, 保存命令行参数
/* Untouched saved command line (eg. for /proc) */
char *saved_command_line;
/* Command line for parameter parsing */
static char *static_command_line;
/* Command line for per-initcall parameter parsing */
static char *initcall_command_line;
static void __init setup_command_line(char *command_line)
{
saved_command_line =
memblock_virt_alloc(strlen(boot_command_line) + 1, 0);
initcall_command_line =
memblock_virt_alloc(strlen(boot_command_line) + 1, 0);
static_command_line = memblock_virt_alloc(strlen(command_line) + 1, 0);
strcpy(saved_command_line, boot_command_line);
strcpy(static_command_line, command_line);
}5.10 设置CPU
setup_nr_cpu_idssetup_per_cpu_areas
/* Setup number of possible processor ids */
int nr_cpu_ids __read_mostly = NR_CPUS;
EXPORT_SYMBOL(nr_cpu_ids);
/* An arch may set nr_cpu_ids earlier if needed, so this would be redundant */
void __init setup_nr_cpu_ids(void)
{
nr_cpu_ids = find_last_bit(cpumask_bits(cpu_possible_mask),NR_CPUS) + 1;
}5.11 smp_prepare_boot_cpu
static inline void set_my_cpu_offset(unsigned long off)
{
/* Set TPIDRPRW */
asm volatile("mcr p15, 0, %0, c13, c0, 4" : : "r" (off) : "memory");
}
void __init smp_prepare_boot_cpu(void)
{
set_my_cpu_offset(per_cpu_offset(smp_processor_id()));
}5.12 build_all_zonelists
启动期间构建zone,
[build_all_zonelists –> build_all_zonelists_init]
/*
* zonelist_order:
* 0 = automatic detection of better ordering.
* 1 = order by ([node] distance, -zonetype)
* 2 = order by (-zonetype, [node] distance)
*
* If not NUMA, ZONELIST_ORDER_ZONE and ZONELIST_ORDER_NODE will create
* the same zonelist. So only NUMA can configure this param.
*/
#define ZONELIST_ORDER_DEFAULT 0
#define ZONELIST_ORDER_NODE 1
#define ZONELIST_ORDER_ZONE 2
/* zonelist order in the kernel.
* set_zonelist_order() will set this to NODE or ZONE.
*/
static int current_zonelist_order = ZONELIST_ORDER_DEFAULT;
static char zonelist_order_name[3][8] = {"Default", "Node", "Zone"};
static void set_zonelist_order(void)
{
current_zonelist_order = ZONELIST_ORDER_ZONE;
}最终调用到build_all_zonelists_init
static noinline void __init build_all_zonelists_init(void)
{
__build_all_zonelists(NULL);
mminit_verify_zonelist();
cpuset_init_current_mems_allowed();
}5.13 page_alloc_init
void __init page_alloc_init(void)
{
hotcpu_notifier(page_alloc_cpu_notify, 0);
}5.14 jump_label_init
/*
* Used to generate warnings if static_key manipulation functions are used
* before jump_label_init is called.
*/
bool static_key_initialized __read_mostly;
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(static_key_initialized);
static __always_inline void jump_label_init(void)
{
static_key_initialized = true;
}5.15 setup_log_buf
设置日志buf
5.16 pidhash_init
struct hlist_head {
struct hlist_node *first;
};
struct hlist_node {
struct hlist_node *next, **pprev;
};
static struct hlist_head *pid_hash;
static unsigned int pidhash_shift = 4;
void __init pidhash_init(void)
{
unsigned int i, pidhash_size;
pid_hash = alloc_large_system_hash("PID", sizeof(*pid_hash), 0, 18,
HASH_EARLY | HASH_SMALL,
&pidhash_shift, NULL,
0, 4096);
pidhash_size = 1U << pidhash_shift;
for (i = 0; i < pidhash_size; i++)
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&pid_hash[i]);
}5.17 vfs_caches_init_early
void __init vfs_caches_init_early(void)
{
dcache_init_early();
inode_init_early();
}5.18 sort_main_extable
异常修复表
struct exception_table_entry
{
unsigned long insn, fixup;
};
extern struct exception_table_entry __start___ex_table[];
extern struct exception_table_entry __stop___ex_table[];
void __init sort_main_extable(void)
{
if (main_extable_sort_needed && __stop___ex_table > __start___ex_table) {
pr_notice("Sorting __ex_table...\n");
sort_extable(__start___ex_table, __stop___ex_table);
}
}
static int cmp_ex(const void *a, const void *b)
{
const struct exception_table_entry *x = a, *y = b;
/* avoid overflow */
if (x->insn > y->insn)
return 1;
if (x->insn < y->insn)
return -1;
return 0;
}
void sort_extable(struct exception_table_entry *start,
struct exception_table_entry *finish)
{
sort(start, finish - start, sizeof(struct exception_table_entry),
cmp_ex, NULL);
}但是这个表定义在什么位置内?
. = ALIGN(4);
__ex_table : AT(ADDR(__ex_table) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__start___ex_table = .;
#ifdef CONFIG_MMU
*(__ex_table)
#endif
__stop___ex_table = .;
}在链接脚本中定义,代表着什么呢?如何定义这个表呢?
大部分都是汇编实现的,当前不进行分析了
# define _ASM_EXTABLE_TYPE(from, to, type) \
.pushsection "__ex_table","a" ; \
.balign 4 ; \
.long (from) - . ; \
.long (to) - . ; \
.long type ; \
.popsection如何调用这个异常修复表呢?
int fixup_exception(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
const struct exception_table_entry *fixup;
fixup = search_exception_tables(instruction_pointer(regs));
if (fixup) {
regs->ARM_pc = fixup->fixup;
#ifdef CONFIG_THUMB2_KERNEL
/* Clear the IT state to avoid nasty surprises in the fixup */
regs->ARM_cpsr &= ~PSR_IT_MASK;
#endif
}
return fixup != NULL;
}调用线路
graph LR fixup_exception --> search_exception_tables --> search_extable --> search_module_extables
5.19 trap_init
中断描述符初始化,但是在arm上初始化好像不是这样进行的
arm上此选项无效
5.20 mm_init
内存分配器初始化(单独分析)
static void __init mm_init(void)
{
/*
* page_ext requires contiguous pages,
* bigger than MAX_ORDER unless SPARSEMEM.
*/
page_ext_init_flatmem();
mem_init();
kmem_cache_init();
percpu_init_late();
pgtable_init();
vmalloc_init();
}5.21 sched_init
调度器初始化(单独分析)
5.22 idr_init_cache
整数ID管理机制
void __init idr_init_cache(void)
{
idr_layer_cache = kmem_cache_create("idr_layer_cache",
sizeof(struct idr_layer), 0, SLAB_PANIC, NULL);
}5.23 rcu_init
void __init rcu_init(void)
{
int cpu;
rcu_bootup_announce();
rcu_init_geometry();
rcu_init_one(&rcu_bh_state, &rcu_bh_data);
rcu_init_one(&rcu_sched_state, &rcu_sched_data);
__rcu_init_preempt();
open_softirq(RCU_SOFTIRQ, rcu_process_callbacks);
/*
* We don't need protection against CPU-hotplug here because
* this is called early in boot, before either interrupts
* or the scheduler are operational.
*/
cpu_notifier(rcu_cpu_notify, 0);
pm_notifier(rcu_pm_notify, 0);
for_each_online_cpu(cpu)
rcu_cpu_notify(NULL, CPU_UP_PREPARE, (void *)(long)cpu);
rcu_early_boot_tests();
}