调度器基础

目录
调度器分为主调度器和周期调度器 但是本节不考虑调度器的具体实现 只进行大方向接口的分析
1 权重计算
1.1 优先级计算
优先级
// 1. 当前优先级normal_prio
p->prio = current->normal_prio;
// 2. 静态优先级
p->static_prio = NICE_TO_PRIO(0)
// 3. 继续计算优先级
p->prio = p->normal_prio = __normal_prio(p);
// 4. 这在计算什么?
#define NICE_TO_PRIO(nice) ((nice) + DEFAULT_PRIO)
#define PRIO_TO_NICE(prio) ((prio) - DEFAULT_PRIO)
static inline int __normal_prio(struct task_struct *p)
{
return p->static_prio;
}1.2 权重计算
struct load_weight {
unsigned long weight;
u32 inv_weight;
};
static void set_load_weight(struct task_struct *p)
{
int prio = p->static_prio - MAX_RT_PRIO;
struct load_weight *load = &p->se.load;
/*
* SCHED_IDLE tasks get minimal weight:
*/
if (p->policy == SCHED_IDLE) {
load->weight = scale_load(WEIGHT_IDLEPRIO);
load->inv_weight = WMULT_IDLEPRIO;
return;
}
load->weight = scale_load(prio_to_weight[prio]);
load->inv_weight = prio_to_wmult[prio];
}
static const int prio_to_weight[40] = {
/* -20 */ 88761, 71755, 56483, 46273, 36291,
/* -15 */ 29154, 23254, 18705, 14949, 11916,
/* -10 */ 9548, 7620, 6100, 4904, 3906,
/* -5 */ 3121, 2501, 1991, 1586, 1277,
/* 0 */ 1024, 820, 655, 526, 423,
/* 5 */ 335, 272, 215, 172, 137,
/* 10 */ 110, 87, 70, 56, 45,
/* 15 */ 36, 29, 23, 18, 15,
};
static const u32 prio_to_wmult[40] = {
/* -20 */ 48388, 59856, 76040, 92818, 118348,
/* -15 */ 147320, 184698, 229616, 287308, 360437,
/* -10 */ 449829, 563644, 704093, 875809, 1099582,
/* -5 */ 1376151, 1717300, 2157191, 2708050, 3363326,
/* 0 */ 4194304, 5237765, 6557202, 8165337, 10153587,
/* 5 */ 12820798, 15790321, 19976592, 24970740, 31350126,
/* 10 */ 39045157, 49367440, 61356676, 76695844, 95443717,
/* 15 */ 119304647, 148102320, 186737708, 238609294, 286331153,
};优先级与负载计算关系 $weight = \frac{1024}{1.25^{nice}}$ ${inv_weight} = \frac{2^{32}}{weight}$
2 调度器类
linux内核充分使用了面向对象的思想,
依靠sched_class将所有的调度器整合
linux上的调度器
| 调度器类 | 描述信息 | 用户接口调度策略 |
|---|---|---|
| dl_sched_class | deadline调度器 | SCHED_DEADLINE |
| rt_sched_class | 实时调度器 | SCHED_FIFO、``SCHED_RR` |
| fair_sched_class | 完全公平调度器 | SCHED_NORMAL、``SCHED_BATCH` |
| idle_sched_class | idle task | SCHED_IDLE |
2.1 调度器类结构体
struct sched_class {
const struct sched_class *next;
void (*enqueue_task) (struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags);
void (*dequeue_task) (struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags);
void (*yield_task) (struct rq *rq);
bool (*yield_to_task) (struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, bool preempt);
void (*check_preempt_curr) (struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags);
/*
* It is the responsibility of the pick_next_task() method that will
* return the next task to call put_prev_task() on the @prev task or
* something equivalent.
*
* May return RETRY_TASK when it finds a higher prio class has runnable
* tasks.
*/
struct task_struct * (*pick_next_task) (struct rq *rq,
struct task_struct *prev);
void (*put_prev_task) (struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p);
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
int (*select_task_rq)(struct task_struct *p, int task_cpu, int sd_flag, int flags);
void (*migrate_task_rq)(struct task_struct *p, int next_cpu);
void (*post_schedule) (struct rq *this_rq);
void (*task_waking) (struct task_struct *task);
void (*task_woken) (struct rq *this_rq, struct task_struct *task);
void (*set_cpus_allowed)(struct task_struct *p,
const struct cpumask *newmask);
void (*rq_online)(struct rq *rq);
void (*rq_offline)(struct rq *rq);
#endif
void (*set_curr_task) (struct rq *rq);
void (*task_tick) (struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int queued);
void (*task_fork) (struct task_struct *p);
void (*task_dead) (struct task_struct *p);
/*
* The switched_from() call is allowed to drop rq->lock, therefore we
* cannot assume the switched_from/switched_to pair is serliazed by
* rq->lock. They are however serialized by p->pi_lock.
*/
void (*switched_from) (struct rq *this_rq, struct task_struct *task);
void (*switched_to) (struct rq *this_rq, struct task_struct *task);
void (*prio_changed) (struct rq *this_rq, struct task_struct *task,
int oldprio);
unsigned int (*get_rr_interval) (struct rq *rq,
struct task_struct *task);
void (*update_curr) (struct rq *rq);
#ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED
void (*task_move_group) (struct task_struct *p, int on_rq);
#endif
};2.2 调度器封装
对调度器进行多态实现;
2.2.1 入队/出队
- enqueue_task
- dequeue_task
static void enqueue_task(struct rq *rq,
struct task_struct *p, int flags)
{
update_rq_clock(rq);
sched_info_queued(rq, p);
p->sched_class->enqueue_task(rq, p, flags);
}
static void dequeue_task(struct rq *rq,
struct task_struct *p, int flags)
{
update_rq_clock(rq);
sched_info_dequeued(rq, p);
p->sched_class->dequeue_task(rq, p, flags);
}2.2.2 激活/销毁
- activate_task
- deactivate_task
void activate_task(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags)
{
if (task_contributes_to_load(p))
rq->nr_uninterruptible--;
enqueue_task(rq, p, flags);
}
void deactivate_task(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags)
{
if (task_contributes_to_load(p))
rq->nr_uninterruptible++;
dequeue_task(rq, p, flags);
}2.2.3 主动放弃
- sched_yield
- yield_to
SYSCALL_DEFINE0(sched_yield)
{
struct rq *rq = this_rq_lock();
schedstat_inc(rq, yld_count);
current->sched_class->yield_task(rq);
/*
* Since we are going to call schedule() anyway, there's
* no need to preempt or enable interrupts:
*/
__release(rq->lock);
spin_release(&rq->lock.dep_map, 1, _THIS_IP_);
do_raw_spin_unlock(&rq->lock);
sched_preempt_enable_no_resched();
schedule();
return 0;
}
int __sched yield_to(struct task_struct *p, bool preempt)
{
struct task_struct *curr = current;
struct rq *rq, *p_rq;
unsigned long flags;
int yielded = 0;
local_irq_save(flags);
rq = this_rq();
again:
p_rq = task_rq(p);
/*
* If we're the only runnable task on the rq and target rq also
* has only one task, there's absolutely no point in yielding.
*/
if (rq->nr_running == 1 && p_rq->nr_running == 1) {
yielded = -ESRCH;
goto out_irq;
}
double_rq_lock(rq, p_rq);
if (task_rq(p) != p_rq) {
double_rq_unlock(rq, p_rq);
goto again;
}
if (!curr->sched_class->yield_to_task)
goto out_unlock;
if (curr->sched_class != p->sched_class)
goto out_unlock;
if (task_running(p_rq, p) || p->state)
goto out_unlock;
yielded = curr->sched_class->yield_to_task(rq, p, preempt);
if (yielded) {
schedstat_inc(rq, yld_count);
/*
* Make p's CPU reschedule; pick_next_entity takes care of
* fairness.
*/
if (preempt && rq != p_rq)
resched_curr(p_rq);
}
out_unlock:
double_rq_unlock(rq, p_rq);
out_irq:
local_irq_restore(flags);
if (yielded > 0)
schedule();
return yielded;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(yield_to);2.2.4 唤醒抢占任务
void check_preempt_curr(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags)
{
const struct sched_class *class;
if (p->sched_class == rq->curr->sched_class) {
rq->curr->sched_class->check_preempt_curr(rq, p, flags);
} else {
for_each_class(class) {
if (class == rq->curr->sched_class)
break;
if (class == p->sched_class) {
resched_curr(rq);
break;
}
}
}
/*
* A queue event has occurred, and we're going to schedule. In
* this case, we can save a useless back to back clock update.
*/
if (task_on_rq_queued(rq->curr) && test_tsk_need_resched(rq->curr))
rq_clock_skip_update(rq, true);
}2.2.5 获取/释放任务
static inline struct task_struct *
pick_next_task(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *prev)
{
const struct sched_class *class = &fair_sched_class;
struct task_struct *p;
/*
* Optimization: we know that if all tasks are in
* the fair class we can call that function directly:
*/
if (likely(prev->sched_class == class &&
rq->nr_running == rq->cfs.h_nr_running)) {
p = fair_sched_class.pick_next_task(rq, prev);
if (unlikely(p == RETRY_TASK))
goto again;
/* assumes fair_sched_class->next == idle_sched_class */
if (unlikely(!p))
p = idle_sched_class.pick_next_task(rq, prev);
return p;
}
again:
for_each_class(class) {
p = class->pick_next_task(rq, prev);
if (p) {
if (unlikely(p == RETRY_TASK))
goto again;
return p;
}
}
BUG(); /* the idle class will always have a runnable task */
}
static inline void put_prev_task(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *prev)
{
prev->sched_class->put_prev_task(rq, prev);
}2.2.6 任务切换
static inline void check_class_changed(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p,
const struct sched_class *prev_class,
int oldprio)
{
if (prev_class != p->sched_class) {
if (prev_class->switched_from)
prev_class->switched_from(rq, p);
/* Possble rq->lock 'hole'. */
p->sched_class->switched_to(rq, p);
} else if (oldprio != p->prio || dl_task(p))
p->sched_class->prio_changed(rq, p, oldprio);
}2.2.7 更新当前任务
unsigned long long task_sched_runtime(struct task_struct *p)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct rq *rq;
u64 ns;
#if defined(CONFIG_64BIT) && defined(CONFIG_SMP)
/*
* 64-bit doesn't need locks to atomically read a 64bit value.
* So we have a optimization chance when the task's delta_exec is 0.
* Reading ->on_cpu is racy, but this is ok.
*
* If we race with it leaving cpu, we'll take a lock. So we're correct.
* If we race with it entering cpu, unaccounted time is 0. This is
* indistinguishable from the read occurring a few cycles earlier.
* If we see ->on_cpu without ->on_rq, the task is leaving, and has
* been accounted, so we're correct here as well.
*/
if (!p->on_cpu || !task_on_rq_queued(p))
return p->se.sum_exec_runtime;
#endif
rq = task_rq_lock(p, &flags);
/*
* Must be ->curr _and_ ->on_rq. If dequeued, we would
* project cycles that may never be accounted to this
* thread, breaking clock_gettime().
*/
if (task_current(rq, p) && task_on_rq_queued(p)) {
update_rq_clock(rq);
p->sched_class->update_curr(rq);
}
ns = p->se.sum_exec_runtime;
task_rq_unlock(rq, p, &flags);
return ns;
}3 任务创建
任务创建是由do_fork进行,与调度器进行沟通的函数是sched_fork,沟通的数据结构是
int sched_fork(unsigned long clone_flags, struct task_struct *p)
{
unsigned long flags;
// #define get_cpu() ({ preempt_disable(); smp_processor_id(); })
// #define put_cpu() preempt_enable()
int cpu = get_cpu(); // 获取CPUID
// 进入内部实现
__sched_fork(clone_flags, p);
/*
* We mark the process as running here. This guarantees that
* nobody will actually run it, and a signal or other external
* event cannot wake it up and insert it on the runqueue either.
*/
p->state = TASK_RUNNING; // 设置运行状态
/*
* Make sure we do not leak PI boosting priority to the child.
*/
p->prio = current->normal_prio; // 复制父优先级到当前
/*
* Revert to default priority/policy on fork if requested.
*/
if (unlikely(p->sched_reset_on_fork)) {
if (task_has_dl_policy(p) || task_has_rt_policy(p)) {
p->policy = SCHED_NORMAL;
p->static_prio = NICE_TO_PRIO(0);
p->rt_priority = 0;
} else if (PRIO_TO_NICE(p->static_prio) < 0)
p->static_prio = NICE_TO_PRIO(0);
p->prio = p->normal_prio = __normal_prio(p);
set_load_weight(p);
/*
* We don't need the reset flag anymore after the fork. It has
* fulfilled its duty:
*/
p->sched_reset_on_fork = 0;
}
if (dl_prio(p->prio)) {
put_cpu();
return -EAGAIN;
} else if (rt_prio(p->prio)) {
p->sched_class = &rt_sched_class;
} else {
p->sched_class = &fair_sched_class;
}
if (p->sched_class->task_fork)
p->sched_class->task_fork(p);
/*
* The child is not yet in the pid-hash so no cgroup attach races,
* and the cgroup is pinned to this child due to cgroup_fork()
* is ran before sched_fork().
*
* Silence PROVE_RCU.
*/
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&p->pi_lock, flags);
set_task_cpu(p, cpu);
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&p->pi_lock, flags);
#if defined(CONFIG_SCHEDSTATS) || defined(CONFIG_TASK_DELAY_ACCT)
if (likely(sched_info_on()))
memset(&p->sched_info, 0, sizeof(p->sched_info));
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_SMP)
p->on_cpu = 0;
#endif
init_task_preempt_count(p);
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
plist_node_init(&p->pushable_tasks, MAX_PRIO);
RB_CLEAR_NODE(&p->pushable_dl_tasks);
#endif
put_cpu();
return 0;
}
static void __sched_fork(unsigned long clone_flags, struct task_struct *p)
{
p->on_rq = 0; // 当前不在队列中
// 设置sched_entity
p->se.on_rq = 0; // 当前不在队列中
p->se.exec_start = 0;
p->se.sum_exec_runtime = 0;
p->se.prev_sum_exec_runtime = 0;
p->se.nr_migrations = 0;
p->se.vruntime = 0;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
p->se.avg.decay_count = 0;
#endif
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->se.group_node);
#ifdef CONFIG_SCHEDSTATS
memset(&p->se.statistics, 0, sizeof(p->se.statistics));
#endif
RB_CLEAR_NODE(&p->dl.rb_node);
init_dl_task_timer(&p->dl);
__dl_clear_params(p);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->rt.run_list);
#ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT_NOTIFIERS
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&p->preempt_notifiers);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA_BALANCING
if (p->mm && atomic_read(&p->mm->mm_users) == 1) {
p->mm->numa_next_scan = jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(sysctl_numa_balancing_scan_delay);
p->mm->numa_scan_seq = 0;
}
if (clone_flags & CLONE_VM)
p->numa_preferred_nid = current->numa_preferred_nid;
else
p->numa_preferred_nid = -1;
p->node_stamp = 0ULL;
p->numa_scan_seq = p->mm ? p->mm->numa_scan_seq : 0;
p->numa_scan_period = sysctl_numa_balancing_scan_delay;
p->numa_work.next = &p->numa_work;
p->numa_faults = NULL;
p->last_task_numa_placement = 0;
p->last_sum_exec_runtime = 0;
p->numa_group = NULL;
#endif /* CONFIG_NUMA_BALANCING */
}分析函数执行
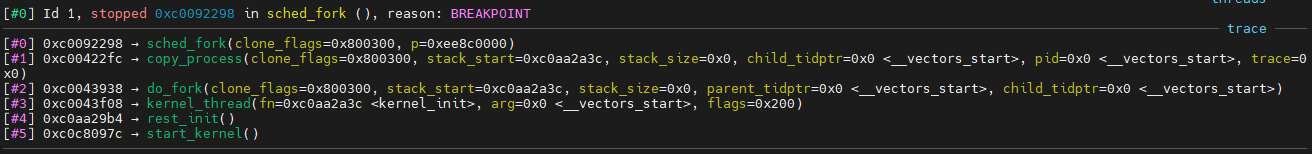
根据上图,我们可以得知创建的是一个线程函数,但是这个不是我们要分析的,我们要分析``sched_fork`函数实现;
- 设置
sched_entity成员 - 设置优先级
- 调用调度器类中的
task_fork函数
执行结束之后
// 将任务添加到调度器
void wake_up_new_task(struct task_struct *p)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct rq *rq;
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&p->pi_lock, flags);
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
/*
* Fork balancing, do it here and not earlier because:
* - cpus_allowed can change in the fork path
* - any previously selected cpu might disappear through hotplug
*/
set_task_cpu(p, select_task_rq(p, task_cpu(p), SD_BALANCE_FORK, 0));
#endif
/* Initialize new task's runnable average */
init_task_runnable_average(p);
rq = __task_rq_lock(p);
activate_task(rq, p, 0); // 激活任务
p->on_rq = TASK_ON_RQ_QUEUED; // 进入队列
trace_sched_wakeup_new(p, true);
check_preempt_curr(rq, p, WF_FORK); // 检查是否可以抢占
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
if (p->sched_class->task_woken)
p->sched_class->task_woken(rq, p);
#endif
task_rq_unlock(rq, p, &flags);
}4 调度基础
- 主调度器
- 滴答调度器
4.1 主调度器
static void __sched __schedule(void)
{
struct task_struct *prev, *next;
unsigned long *switch_count;
struct rq *rq;
int cpu;
preempt_disable();
cpu = smp_processor_id();
rq = cpu_rq(cpu);
rcu_note_context_switch();
prev = rq->curr;
schedule_debug(prev);
if (sched_feat(HRTICK))
hrtick_clear(rq);
/*
* Make sure that signal_pending_state()->signal_pending() below
* can't be reordered with __set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE)
* done by the caller to avoid the race with signal_wake_up().
*/
smp_mb__before_spinlock();
raw_spin_lock_irq(&rq->lock);
rq->clock_skip_update <<= 1; /* promote REQ to ACT */
switch_count = &prev->nivcsw;
if (prev->state && !(preempt_count() & PREEMPT_ACTIVE)) {
if (unlikely(signal_pending_state(prev->state, prev))) {
prev->state = TASK_RUNNING;
} else {
deactivate_task(rq, prev, DEQUEUE_SLEEP);
prev->on_rq = 0;
/*
* If a worker went to sleep, notify and ask workqueue
* whether it wants to wake up a task to maintain
* concurrency.
*/
if (prev->flags & PF_WQ_WORKER) {
struct task_struct *to_wakeup;
to_wakeup = wq_worker_sleeping(prev, cpu);
if (to_wakeup)
try_to_wake_up_local(to_wakeup);
}
}
switch_count = &prev->nvcsw;
}
if (task_on_rq_queued(prev))
update_rq_clock(rq);
next = pick_next_task(rq, prev);
clear_tsk_need_resched(prev);
clear_preempt_need_resched();
rq->clock_skip_update = 0;
if (likely(prev != next)) {
rq->nr_switches++;
rq->curr = next;
++*switch_count;
rq = context_switch(rq, prev, next); /* unlocks the rq */
cpu = cpu_of(rq);
} else
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&rq->lock);
post_schedule(rq);
sched_preempt_enable_no_resched();
}graph TD schedule --> __schedule --> context_switch
进入任务切换的核心函数context_switch,这个函数真够复杂的;
static inline struct rq *context_switch(struct rq *rq,
struct task_struct *prev,
struct task_struct *next)
{
struct mm_struct *mm, *oldmm;
// 执行切换前准备
prepare_task_switch(rq, prev, next);
// 普通进程mm和active_mm相等
// 但是内核线程没有mm,只有active_mm
mm = next->mm;
oldmm = prev->active_mm;
arch_start_context_switch(prev);
if (!mm) { // 这个是内核线程
next->active_mm = oldmm; // next线程借用oldmem,什么原因
atomic_inc(&oldmm->mm_count); // 减少计数
enter_lazy_tlb(oldmm, next); // 进入lazytlb,arm上为空
} else // 这个是用户线程
switch_mm(oldmm, mm, next);
if (!prev->mm) { // 代表prev是一个内核线程
prev->active_mm = NULL;
rq->prev_mm = oldmm; // 内核线程共享内存
}
/*
* Since the runqueue lock will be released by the next
* task (which is an invalid locking op but in the case
* of the scheduler it's an obvious special-case), so we
* do an early lockdep release here:
*/
spin_release(&rq->lock.dep_map, 1, _THIS_IP_);
context_tracking_task_switch(prev, next); // 调试使用
/* Here we just switch the register state and the stack. */
switch_to(prev, next, prev); // 这个函数和体系相关
barrier();
return finish_task_switch(prev);
}
extern struct task_struct *__switch_to(struct task_struct *,
struct thread_info *,
struct thread_info *);
#define switch_to(prev,next,last) \
do { \
last = __switch_to(prev,task_thread_info(prev), task_thread_info(next)); \
} while (0)在arm32的实现中,这个是汇编编写的;我并没有看明白 这个地方和硬件进行强相关;
最终需要考虑的是进程在队列中的实现;
4.2 内存空间切换switch_mm
当然也是和硬件体系强相关
static inline void
switch_mm(struct mm_struct *prev, struct mm_struct *next,
struct task_struct *tsk)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_MMU
unsigned int cpu = smp_processor_id();
/*
* __sync_icache_dcache doesn't broadcast the I-cache invalidation,
* so check for possible thread migration and invalidate the I-cache
* if we're new to this CPU.
*/
if (cache_ops_need_broadcast() &&
!cpumask_empty(mm_cpumask(next)) &&
!cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, mm_cpumask(next)))
__flush_icache_all();
if (!cpumask_test_and_set_cpu(cpu, mm_cpumask(next)) || prev != next) {
check_and_switch_context(next, tsk);
if (cache_is_vivt())
cpumask_clear_cpu(cpu, mm_cpumask(prev));
}
#endif
}4.3 滴答调度器
void scheduler_tick(void)
{
int cpu = smp_processor_id();
struct rq *rq = cpu_rq(cpu);
struct task_struct *curr = rq->curr;
sched_clock_tick();
raw_spin_lock(&rq->lock);
update_rq_clock(rq);
curr->sched_class->task_tick(rq, curr, 0);
update_cpu_load_active(rq);
raw_spin_unlock(&rq->lock);
perf_event_task_tick();
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
rq->idle_balance = idle_cpu(cpu);
trigger_load_balance(rq);
#endif
rq_last_tick_reset(rq);
}5 就绪队列
5.1 成员分析
struct rq {
/* runqueue lock: */
raw_spinlock_t lock;
/*
* nr_running and cpu_load should be in the same cacheline because
* remote CPUs use both these fields when doing load calculation.
*/
unsigned int nr_running;
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA_BALANCING
unsigned int nr_numa_running;
unsigned int nr_preferred_running;
#endif
#define CPU_LOAD_IDX_MAX 5
unsigned long cpu_load[CPU_LOAD_IDX_MAX];
unsigned long last_load_update_tick;
#ifdef CONFIG_NO_HZ_COMMON
u64 nohz_stamp;
unsigned long nohz_flags;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NO_HZ_FULL
unsigned long last_sched_tick;
#endif
/* capture load from *all* tasks on this cpu: */
struct load_weight load;
unsigned long nr_load_updates;
u64 nr_switches;
struct cfs_rq cfs;
struct rt_rq rt;
struct dl_rq dl;
#ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED
/* list of leaf cfs_rq on this cpu: */
struct list_head leaf_cfs_rq_list;
struct sched_avg avg;
#endif /* CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED */
/*
* This is part of a global counter where only the total sum
* over all CPUs matters. A task can increase this counter on
* one CPU and if it got migrated afterwards it may decrease
* it on another CPU. Always updated under the runqueue lock:
*/
unsigned long nr_uninterruptible;
struct task_struct *curr, *idle, *stop;
unsigned long next_balance;
struct mm_struct *prev_mm;
unsigned int clock_skip_update;
u64 clock;
u64 clock_task;
atomic_t nr_iowait;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
struct root_domain *rd;
struct sched_domain *sd;
unsigned long cpu_capacity;
unsigned char idle_balance;
/* For active balancing */
int post_schedule;
int active_balance;
int push_cpu;
struct cpu_stop_work active_balance_work;
/* cpu of this runqueue: */
int cpu;
int online;
struct list_head cfs_tasks;
u64 rt_avg;
u64 age_stamp;
u64 idle_stamp;
u64 avg_idle;
/* This is used to determine avg_idle's max value */
u64 max_idle_balance_cost;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_TIME_ACCOUNTING
u64 prev_irq_time;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PARAVIRT
u64 prev_steal_time;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PARAVIRT_TIME_ACCOUNTING
u64 prev_steal_time_rq;
#endif
/* calc_load related fields */
unsigned long calc_load_update;
long calc_load_active;
#ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_HRTICK
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
int hrtick_csd_pending;
struct call_single_data hrtick_csd;
#endif
struct hrtimer hrtick_timer;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SCHEDSTATS
/* latency stats */
struct sched_info rq_sched_info;
unsigned long long rq_cpu_time;
/* could above be rq->cfs_rq.exec_clock + rq->rt_rq.rt_runtime ? */
/* sys_sched_yield() stats */
unsigned int yld_count;
/* schedule() stats */
unsigned int sched_count;
unsigned int sched_goidle;
/* try_to_wake_up() stats */
unsigned int ttwu_count;
unsigned int ttwu_local;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
struct llist_head wake_list;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_IDLE
/* Must be inspected within a rcu lock section */
struct cpuidle_state *idle_state;
#endif
};系统中每一个CPU都存在一个就绪队列,一个percpu变量.
#define DEFINE_PER_CPU_SHARED_ALIGNED(type, name) \
DEFINE_PER_CPU_SECTION(type, name, PER_CPU_SHARED_ALIGNED_SECTION) \
____cacheline_aligned_in_smp
DEFINE_PER_CPU_SHARED_ALIGNED(struct rq, runqueues);操作宏
DECLARE_PER_CPU_SHARED_ALIGNED(struct rq, runqueues);
#define cpu_rq(cpu) (&per_cpu(runqueues, (cpu)))
#define this_rq() this_cpu_ptr(&runqueues)
#define task_rq(p) cpu_rq(task_cpu(p))
#define cpu_curr(cpu) (cpu_rq(cpu)->curr)
#define raw_rq() raw_cpu_ptr(&runqueues)设置当前运行队列的任务
5.2 操作函数
void update_rq_clock(struct rq *rq)
{
s64 delta;
lockdep_assert_held(&rq->lock);
if (rq->clock_skip_update & RQCF_ACT_SKIP)
return;
delta = sched_clock_cpu(cpu_of(rq)) - rq->clock;
if (delta < 0)
return;
rq->clock += delta;
update_rq_clock_task(rq, delta);
}6 调度增强
6.1 组调度
组调度:多个用户登录时平均分配计算机时间;
/* task group related information */
struct task_group {
struct cgroup_subsys_state css;
#ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED
/* schedulable entities of this group on each cpu */
struct sched_entity **se;
/* runqueue "owned" by this group on each cpu */
struct cfs_rq **cfs_rq;
unsigned long shares;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
atomic_long_t load_avg;
atomic_t runnable_avg;
#endif
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_RT_GROUP_SCHED
struct sched_rt_entity **rt_se;
struct rt_rq **rt_rq;
struct rt_bandwidth rt_bandwidth;
#endif
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct list_head list;
struct task_group *parent;
struct list_head siblings;
struct list_head children;
#ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_AUTOGROUP
struct autogroup *autogroup;
#endif
struct cfs_bandwidth cfs_bandwidth;
};


